Navigate your HubSpot migration with confidence by understanding the true complexity of re-platforming and leveraging strategic planning tools to prevent budget overruns, timeline delays, and data integrity issues.
Table of Contents
- The Hidden Complexity of HubSpot Migration
- Why Traditional Migration Planning Falls Short
- The Real Costs of Underestimating Migration Scope
- Common Migration Pitfalls That Derail Projects
- Strategic Pre-Migration Assessment Framework
- Data Mapping: The Foundation of Migration Success
- Asset Inventory and Prioritization Strategy
- Integration Planning and Technical Debt Management
- Building Accurate Timeline and Cost Projections
- Leveraging Automation for Migration Planning
- Post-Migration Optimization and Continuous Improvement
- Frequently Asked Questions
Re-platforming to HubSpot represents a transformative opportunity for businesses seeking to consolidate their marketing, sales, and service operations into a unified ecosystem. The promise is compelling: streamlined workflows, centralized data, powerful automation capabilities, and actionable insights that drive growth. However, the path from legacy systems to HubSpot's integrated platform is fraught with challenges that even experienced teams often underestimate.
The statistics tell a sobering story. Industry research indicates that 40-60% of CRM migration projects exceed their original budgets, while nearly half experience significant timeline delays. More concerning, approximately 30% of organizations report ongoing data quality issues stemming from poorly executed migrations. These failures don't just represent financial waste—they erode team confidence, disrupt customer relationships, and can set digital transformation initiatives back by months or years.
What separates successful HubSpot migrations from failed attempts? The answer lies not in execution prowess or technical expertise alone, but in comprehensive planning that occurs long before the first data record moves. Organizations that invest in thorough pre-migration assessment and leverage modern planning tools to understand the true scope of their migration consistently achieve better outcomes at lower costs than those who rush into execution.
The Hidden Complexity of HubSpot Migration
Beyond Simple Data Transfer
Many businesses approach HubSpot migration with a dangerously simplistic mental model: export data from the old system, import it into HubSpot, configure a few settings, and you're done. This "lift and shift" mentality represents one of the most common and expensive misconceptions in enterprise software transitions.
Modern CRM migrations involve far more than moving contact records from point A to point B. Each organization has accumulated years of custom workflows, automation rules, integration dependencies, and business logic embedded within their current platform. These invisible assets often represent more work to recreate than the visible data everyone focuses on.
Consider a mid-sized B2B company migrating from Marketo to HubSpot. Their Marketo instance contains 150,000 contact records—a manageable data volume. However, beneath this surface lies a complex web of 200+ email templates, 75 landing pages, 120 active workflows, 45 forms, 30 smart lists, and integrations with Salesforce, Zoom, and their webinar platform. Each of these elements requires careful analysis, strategic decision-making, and reconstruction in HubSpot's environment.
The business logic embedded in these assets—scoring rules, segmentation criteria, lead routing workflows—represents institutional knowledge accumulated over years. Losing this logic during migration or failing to translate it appropriately to HubSpot's different architecture can devastate marketing and sales effectiveness.
Platform Architecture Differences
Marketo, Pardot, and HubSpot may all serve similar high-level purposes, but their architectural approaches differ significantly. What takes three clicks and a simple rule in one platform might require a complex workflow and custom property setup in another. These architectural differences create translation challenges that extend far beyond data field mapping.
For instance, Pardot's concept of prospects differs fundamentally from HubSpot's contact model. Marketo's program structure doesn't map directly to HubSpot's campaigns. These aren't mere semantic differences—they represent fundamentally different approaches to organizing marketing operations that require strategic thinking to bridge effectively.
Organizations that don't account for these architectural differences during planning inevitably discover them mid-migration when it's expensive and disruptive to address them. Understanding platform differences before migration begins transforms an emergency into a planned adaptation.
Why Traditional Migration Planning Falls Short
The Spreadsheet Approach
When faced with a migration project, most teams reach for familiar tools: spreadsheets, manual inventories, and back-of-the-envelope calculations. A project manager creates a comprehensive spreadsheet listing all the assets to migrate, estimates hours for each, applies rough hourly rates, and arrives at a budget number. This approach feels methodical and thorough.
In reality, manual planning systematically underestimates complexity for several predictable reasons. First, it's nearly impossible to manually inventory every asset in a mature marketing automation platform. That workflow you built three years ago for a one-off campaign? It's still running in the background, influencing lead scores and triggering actions. The manual inventory misses it.
Second, spreadsheet planning relies on linear time estimates that don't account for dependencies, testing cycles, and rework. Rebuilding an email template might take two hours in isolation, but what about testing it across email clients, ensuring brand consistency, and revising based on stakeholder feedback? The two-hour estimate becomes eight when reality intrudes.
Third, manual estimates struggle with cumulative complexity. Rebuilding five workflows might take ten hours each—50 hours total. But what if those workflows interact, share dependencies, or require testing in combination? The actual effort could easily reach 75-100 hours due to these interaction effects that spreadsheet planning doesn't capture.
The "Figure It Out As We Go" Trap
Some organizations take an even less structured approach, embracing an agile mindset that assumes flexibility will overcome planning deficiencies. The logic goes: "We can't predict every challenge, so let's start migrating and adapt as issues arise."
This approach might work for greenfield software development where you're creating something new and can iterate toward a solution. Migration is fundamentally different—you're moving existing business-critical operations with zero tolerance for data loss or extended downtime. The "figure it out" approach transforms predictable challenges into emergencies that must be solved under pressure.
When you discover mid-migration that your lead scoring model can't be directly replicated in HubSpot, you're forced into rushed decision-making about alternative approaches. These pressure-cooker decisions rarely produce optimal solutions. They're good enough to keep the project moving, but they create technical debt that haunts operations for years.
Organizations that underinvest in planning consistently pay multiples of those savings in extended timelines, consultant fees to fix problems, and opportunity costs from degraded system functionality during extended transition periods.
The Real Costs of Underestimating Migration Scope
Budget Overruns and Timeline Delays
When migration projects go over budget, the financial impact extends beyond the direct overspend. Organizations typically fund migrations by reallocating budget from other initiatives, expecting to recoup this investment through the new platform's efficiencies within 12-18 months. Budget overruns extend this payback period, sometimes indefinitely.
A migration project budgeted at $50,000 that eventually costs $85,000 doesn't just represent a $35,000 overrun. It means other planned initiatives lost their funding, opportunity costs from delayed system benefits, and potential emergency budget reallocations that disrupt financial planning. The true cost of budget overruns often reaches 2-3x the nominal dollar amount when you account for these cascading effects.
Timeline delays create their own category of damage. When a migration scheduled for Q2 completion slides into Q4, sales and marketing teams operate for six extra months in a system everyone knows is being replaced. User engagement declines, process improvements get postponed, and strategic initiatives wait for "after the migration." This organizational limbo creates invisible productivity costs that never appear in project accounting.
Data Integrity Issues
Poor migration planning commonly manifests as data quality problems that emerge after go-live. Duplicate records proliferate when deduplication rules weren't properly defined. Field mapping errors create nonsensical data combinations. Historical activity records get orphaned when relationship mappings fail.
These data integrity issues aren't merely aesthetic problems—they actively undermine business operations. Sales representatives waste time sorting through duplicate contacts. Marketing segmentation produces inaccurate audiences because field data doesn't mean what marketers think it means. Reports generate misleading insights because historical data wasn't properly aligned.
The average cost to correct post-migration data quality issues ranges from $15,000 to $75,000 depending on data volume and corruption severity. This doesn't account for the opportunity costs from inaccurate segmentation, flawed reporting, and lost trust in the CRM as a system of record.
Organizations that discover major data integrity issues six months post-migration face an agonizing decision: live with corrupted data and work around it, or conduct a partial re-migration to fix the issues—essentially paying twice to do the job properly.
User Adoption Challenges
Inadequate planning creates user adoption problems through several mechanisms. When asset rebuilding takes longer than expected, training gets compressed or delayed. Users onboard to a system that's still being configured, creating confusion and frustration. Key workflows remain incomplete, forcing users into manual workarounds that become habits resistant to change.
Users who encounter a half-baked implementation during initial exposure develop lasting negative impressions. First impressions matter enormously in technology adoption. Organizations have essentially one chance to launch a new CRM successfully. A bungled launch due to poor planning creates resistance that persists long after technical issues get resolved.
The productivity impact of low user adoption can exceed the entire migration cost. When sales teams don't fully utilize CRM capabilities, deal visibility suffers, forecasting accuracy declines, and revenue leaks through cracks in the process. Marketing automation that doesn't get leveraged represents wasted platform investment beyond the migration expense.
Common Migration Pitfalls That Derail Projects
Pitfall #1: Incomplete Asset Discovery
The most fundamental migration planning failure is incomplete discovery of what actually needs to migrate. Marketing automation platforms accumulate digital assets organically over years. Campaign templates built for a single event three years ago often remain in the system, potentially still referenced by active workflows.
These hidden assets create problems when they're discovered mid-migration. The project scope didn't include them, so no time or budget was allocated. Yet they can't be ignored because they're actively used or referenced by other assets. The discovery triggers an emergency assessment: Do we need this? How much work to rebuild it? Can we live without it?
Each mid-migration asset discovery creates delays, budget pressures, and scope negotiation friction between stakeholders. These disruptions compound, transforming a planned project into a reactive firefighting exercise.
Comprehensive pre-migration asset discovery using automated tools rather than manual inventory eliminates these surprises. Understanding exactly what exists in your current platform before committing to a migration plan prevents the discovery-crisis-adaptation cycle that characterizes poorly planned migrations.
Pitfall #2: Underestimating Integration Complexity
Modern marketing automation platforms don't operate in isolation—they're nodes in a complex web of integrated systems. CRM platforms, webinar tools, form builders, analytics platforms, advertising systems, and dozens of other applications connect to create your marketing technology stack.
Each integration represents dependencies that must be addressed during migration. Some integrations have HubSpot equivalents that can be reconfigured relatively easily. Others require custom development work. Still others might need complete re-architecture because HubSpot's integration approach differs fundamentally from your current platform.
Organizations that don't inventory and assess integrations during planning discover them when critical business processes break post-migration. Your webinar registration workflow stopped working? That's because the integration that pushed registrants to your marketing automation platform needs complete reconfiguration for HubSpot.
Integration issues are particularly expensive because they often emerge after go-live when you're operating under the pressure of broken business processes. Emergency integration fixes cost 3-5x what planned integration work would have cost, and they're typically lower quality due to time pressure.
Pitfall #3: Treating All Assets Equally
Not every asset in your current platform deserves migration. That campaign landing page from 2019? Your business has probably evolved beyond its messaging. The email template that consistently delivers poor open rates? Migration might be an opportunity to kill it rather than perpetuate mediocrity.
However, without strategic asset assessment during planning, teams default to migrating everything. This "preserve everything" mentality stems from reasonable caution—better to have it and not need it than need it and not have it. But comprehensive migration of every historical asset dramatically increases project scope, cost, and complexity.
Strategic asset prioritization during planning can reduce migration scope by 30-50% by identifying what genuinely needs to move versus what can be archived or abandoned. This requires business judgment, not just technical inventory—evaluating asset performance, strategic alignment, and ongoing relevance.
The time to make these strategic decisions is during planning when you can analyze calmly, consult stakeholders, and make thoughtful choices. Mid-migration, these become rushed yes/no decisions without adequate analysis.
Pitfall #4: Ignoring Data Relationships
Data in CRM systems exists in complex webs of relationships. Contacts associate with companies. Deals link to contacts. Activities connect to deals. Custom objects relate to multiple other objects. These relationships create data dependencies that must be preserved during migration for the system to remain functional.
Relationship mapping often receives inadequate attention during planning because it's invisible. When you look at a contact record, you see name, email, job title—concrete fields that obviously need to map to equivalents in HubSpot. The relationships that contact has to deals, activities, and other objects? Less visible, therefore less likely to be carefully planned.
Post-migration relationship failures create orphaned records, broken reporting, and operational confusion. Marketing can't identify which contacts are associated with open opportunities. Sales can't see the complete history of interactions with a prospect. Reports that should aggregate data across relationships return incomplete results.
Proper relationship mapping during planning requires understanding the entity relationship diagram of both your current platform and HubSpot, then architecting how to preserve or translate these relationships during migration. This technical work can't be rushed or improvised—it requires systematic analysis during the planning phase.
Strategic Pre-Migration Assessment Framework
Conducting a Comprehensive System Audit
Effective migration planning begins with a thorough audit of your current system—not just the data, but the complete operational architecture. This audit serves multiple purposes: creating an accurate asset inventory, identifying technical debt that shouldn't migrate, and establishing baseline metrics for measuring migration success.
A comprehensive audit should inventory all of the following categories:
Data Assets: Contacts, companies, deals, custom objects, and their associated properties. Document record volumes, data quality indicators (completion rates, duplicate percentages), and relationship structures. Understanding your data landscape prevents mid-migration surprises about volume, complexity, or quality issues.
Marketing Assets: Email templates, landing pages, forms, website pages, calls-to-action, and any other marketing collateral managed within the platform. For each asset category, document quantities, usage patterns, and performance metrics. This data informs strategic decisions about what deserves migration effort.
Automation and Workflows: Document every workflow, automation rule, and smart list. Map their triggers, actions, and dependencies on other system elements. This creates a blueprint for rebuilding automation logic in HubSpot, accounting for architectural differences between platforms.
Integrations and Extensions: Catalog every integration with external systems, including native platform integrations, API connections, and third-party middleware. Document data flow directions, synchronization frequency, and business processes dependent on each integration.
Reports and Dashboards: Inventory reporting assets, the data sources they draw from, and who uses them regularly. Understanding reporting requirements helps prioritize which historical data truly needs to migrate versus what can be archived.
User Roles and Permissions: Document current user access patterns, roles, and permission structures. This informs HubSpot configuration to maintain appropriate data access controls post-migration.
Data Quality Assessment and Remediation Planning
Your current platform's data quality directly impacts migration complexity and cost. Organizations often discover their data quality is worse than assumed once systematic assessment begins. A comprehensive data quality audit typically reveals that 30-40% of records require some form of cleansing or enrichment.
Conduct targeted data quality analysis across multiple dimensions:
Completeness: What percentage of records have values in critical fields? Missing phone numbers, job titles, or company associations create functional gaps that undermine HubSpot's utility post-migration.
Accuracy: When was data last verified? Contact information decays at approximately 25-30% annually as people change jobs, companies relocate, and phone numbers change. Old data might be complete but inaccurate.
Consistency: Do you have standardized formats for company names, addresses, and custom fields? Inconsistency creates deduplication problems and reporting inaccuracies. "IBM," "International Business Machines," and "IBM Corporation" might all reference the same company but won't be recognized as such without standardization.
Duplication: How many duplicate records exist? Duplicates emerge from multiple lead capture sources, CRM data imports, and manual entry over time. Migration provides an opportunity to deduplicate, but only if you identify the problem during planning.
Based on quality assessment findings, develop a data remediation plan that addresses issues before migration. Cleaning data in your current system is almost always easier and less expensive than trying to clean it during or after migration.
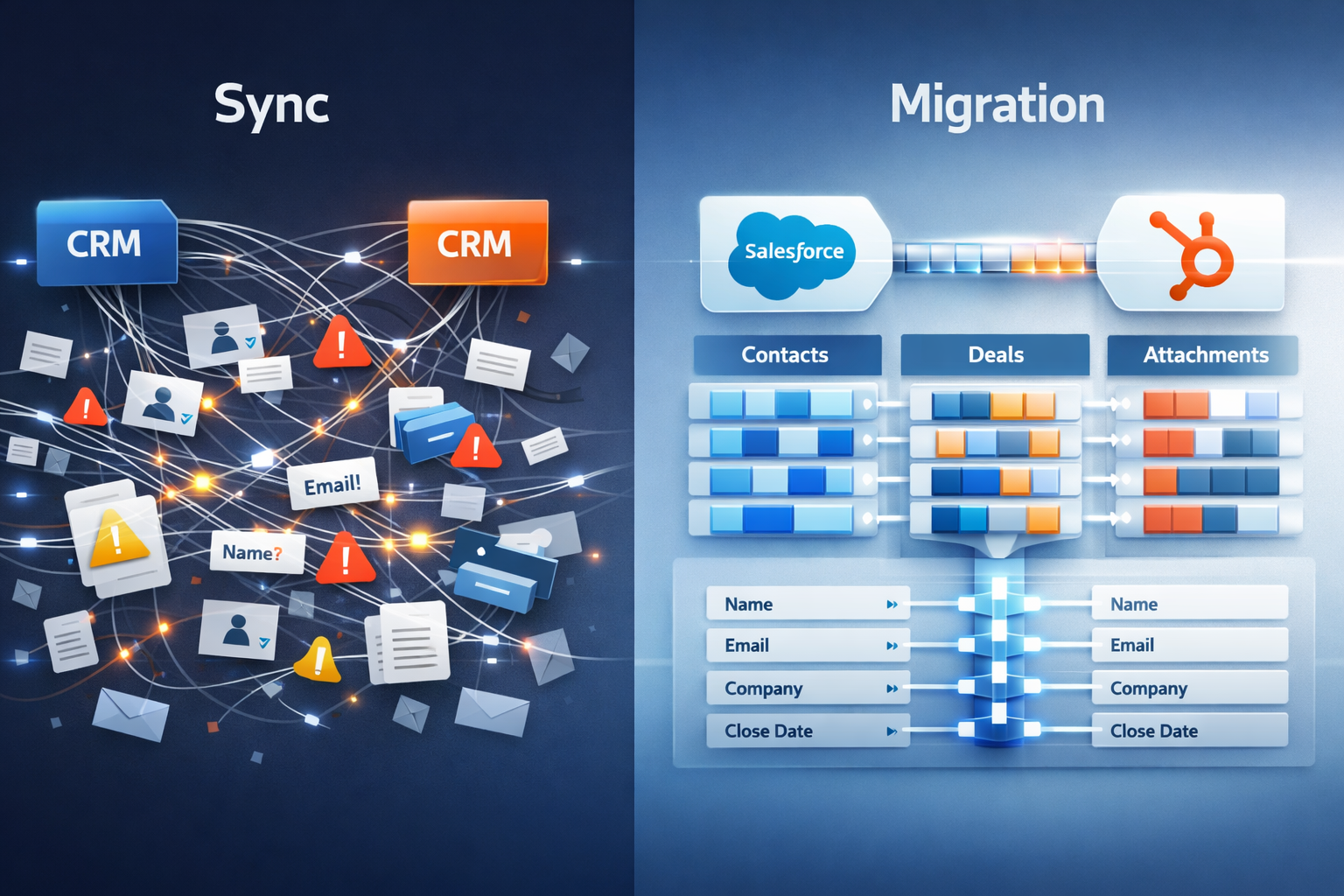
Data Mapping: The Foundation of Migration Success
Understanding Object and Field Relationships
Data mapping represents the technical translation layer between your current platform's data model and HubSpot's. This isn't simply matching "First Name" field to "First Name" field—it requires understanding how different platforms conceptualize and organize information.
Effective data mapping starts with understanding object models in both systems. Your current platform might organize information around "Leads" and "Accounts" while HubSpot uses "Contacts" and "Companies." These aren't just different names for the same concepts—they represent different architectural philosophies that require thoughtful translation.
Custom objects add another complexity layer. If you've built custom objects in your current platform to track specific business information, you need to decide whether to recreate these as custom objects in HubSpot, map them to standard objects, or find alternative approaches using HubSpot's native features.
Field-level mapping requires attention to both data types and business logic. A text field in your current platform might map to a dropdown property in HubSpot if the text values represent a limited set of options. This transformation improves data consistency but requires enumeration of all possible values during planning.
Handling Complex Data Transformations
Some data transformations during migration go beyond simple field-to-field mapping. You might need to combine multiple source fields into a single target field, split data from one field into multiple HubSpot properties, or apply business logic to derive new property values from existing data.
For example, your current platform might track lead status in a single field with 15 possible values. HubSpot's lifecycle stages work differently, requiring you to map those 15 statuses to HubSpot's standard stages, potentially with custom sub-stages. This mapping requires business judgment—understanding what each status means operationally and how it translates to HubSpot's model.
Date field transformations often create unexpected complexity. Different platforms may store dates in different formats, time zones, or even different date standards (Unix timestamps versus formatted dates). Ensuring date data translates accurately prevents timeline confusion in historical records.
Complex transformations need to be fully specified during planning, not improvised during migration execution. Each transformation rule should be documented, tested with sample data, and validated by business stakeholders before implementation.
Preserving Historical Data Integrity
Historical data presents unique challenges during migration. Unlike current operational data that gets actively used and refined, historical records accumulate over years with fields that may no longer exist, values that don't match current standards, and relationships to now-obsolete objects.
Organizations face a strategic choice: invest significant effort to migrate and normalize all historical data, or selectively migrate recent history while archiving older records for reference. This decision should be driven by actual business needs, not emotional attachment to data completeness.
Most businesses find that 80% of value comes from 20% of their historical data—typically the most recent 18-24 months. Older historical records might be preserved for compliance or reference but don't need to reside in your active HubSpot environment where they add complexity and cost.
When migrating historical data, pay special attention to preserving timeline accuracy. Activity timestamps, deal stage progression dates, and email engagement history create narrative context essential for understanding customer relationships. Losing these temporal relationships transforms rich historical context into meaningless disconnected events.
Asset Inventory and Prioritization Strategy
Categorizing Assets by Business Value
Not all marketing assets deliver equivalent business value. Some email templates drive 40% of your lead generation. Others haven't been used in 18 months. Strategic migration planning requires distinguishing between these categories and allocating effort accordingly.
Develop a framework for categorizing assets across multiple dimensions:
Usage Frequency: How often is this asset used? Daily, weekly, monthly, rarely, or never? High-frequency assets obviously deserve migration priority. Zero-use assets might not need to migrate at all.
Business Impact: What role does this asset play in critical business processes? An email sequence that's part of your core lead nurturing program has higher business impact than a one-off announcement template.
Performance Quality: Does this asset perform well? Email templates with strong open and click rates deserve recreation in HubSpot. Consistently underperforming assets might be better retired than migrated.
Maintenance Requirements: How much ongoing upkeep does this asset need? Some templates require constant customization for each use while others work perfectly as-is. High-maintenance assets might be candidates for redesign during migration rather than direct recreation.
Dependency Complexity: How many other assets or workflows depend on this element? Forms referenced by 20 different landing pages need careful migration planning. Standalone assets have fewer dependencies to manage.
Creating Migration Priority Tiers
Based on your asset categorization, establish clear priority tiers that guide migration execution:
Tier 1 - Critical Path Assets: Elements essential for basic business operations that must migrate first. This typically includes core lead capture forms, primary email templates for automated nurture sequences, and critical landing pages for ongoing campaigns.
Tier 2 - Important Supporting Assets: Elements that enhance operations but aren't immediately essential. This might include secondary email templates, historical landing pages that still receive traffic, and supplementary workflow automations.
Tier 3 - Nice-to-Have Assets: Elements that provide value but could be recreated if needed. This category includes specialized templates used occasionally, archived campaign materials that might be referenced, and experimental workflows under development.
Tier 4 - Archive Candidates: Assets that probably don't need to migrate but should be preserved for reference. This includes obsolete templates, deprecated workflows, and historical campaign materials relevant for performance analysis but not active use.
This tiered approach allows phased migration where critical assets move first, enabling business operations to continue while lower-priority elements migrate subsequently. It also provides natural breakpoints if budget constraints require scaling back scope—lower tiers can be deferred without impacting core operations.
Identifying Opportunities for Improvement
Migration provides a natural opportunity to improve assets rather than simply recreating them as-is. An email template that's served adequately for three years might benefit from modern design improvements, better mobile responsiveness, or enhanced personalization capabilities available in HubSpot.
Treat migration as a chance to implement improvements you've been deferring. That landing page with mediocre conversion rates? Redesign it according to current best practices during recreation. The workflow with confusing logic? Simplify and optimize it for HubSpot's architecture.
However, improvement opportunities create scope creep risks if not managed carefully. Distinguish between essential improvements that should happen during migration and nice-to-have enhancements better deferred to post-migration optimization. The goal is selective improvement where obvious wins can be captured without derailing timeline and budget.
Document improvement opportunities identified during planning. Those deferred for post-migration become a ready backlog of enhancements once your team has adapted to HubSpot's environment and operations have stabilized.
Integration Planning and Technical Debt Management
Mapping Integration Dependencies
Your marketing automation platform likely serves as a central hub connecting numerous other business systems. Each integration represents a potential failure point during migration if not properly planned.
Create a comprehensive integration dependency map documenting:
Source and Destination Systems: What systems does your marketing automation platform exchange data with? This includes obvious connections like your CRM, but also webinar platforms, form builders, advertising systems, analytics tools, and less obvious connections.
Data Flow Direction: Does data flow one-way or bidirectional between systems? Bidirectional integrations have higher complexity and greater failure risk during migration transitions.
Synchronization Timing: Does data sync in real-time, hourly, daily, or on-demand? Real-time integrations require careful cutover planning to prevent data loss during the transition window.
Business Process Dependencies: What business processes depend on each integration? Understanding the operational impact of integration disruptions helps prioritize which connections must be maintained during migration versus those that can experience brief interruptions.
Integration Mechanism: How is the integration implemented? Native platform integrations, third-party middleware, custom API code, or manual CSV exports all require different migration approaches.
Assessing HubSpot Integration Capabilities
Not every integration from your current platform has a direct equivalent in HubSpot. The migration planning phase is when you discover and address these gaps, not during execution when they become emergencies.
For each integration, assess:
Native HubSpot Support: Does HubSpot offer native integration with this system? Native integrations typically migrate more easily and reliably than custom connections.
Marketplace Solutions: If no native integration exists, are there third-party solutions in HubSpot's marketplace that provide the needed connectivity? Evaluate these options for capability match and cost implications.
Custom Development Requirements: For integrations without native or marketplace solutions, what custom development would be required? This becomes a budget and timeline consideration during planning.
Alternative Approaches: Could HubSpot's native features replace the need for this integration? Sometimes integration dependencies stem from feature gaps in your current platform that HubSpot addresses natively.
Middleware Solutions: For complex integration scenarios, middleware platforms like SyncMatters can maintain multiple system connections through a centralized hub, simplifying migration coordination across systems.
Managing and Reducing Technical Debt
Most mature marketing automation implementations carry significant technical debt—custom code, workarounds for platform limitations, and accumulated integration complexity that would be better eliminated than migrated.
Migration provides a natural opportunity to pay down technical debt rather than carrying it forward into your new platform. However, this requires intentional planning to distinguish between debt that should be eliminated and valuable customization worth preserving.
Categories of technical debt commonly found in marketing automation platforms:
Workaround Workflows: Automation sequences created to work around platform limitations that HubSpot might address natively. Identify these during planning to simplify your migrated environment.
Obsolete Custom Code: Snippets and scripts written years ago for specific needs that may no longer be relevant. Audit custom code for ongoing value before deciding to port it to HubSpot.
Integration Redundancy: Multiple overlapping integrations that evolved organically rather than being architected coherently. Migration planning can consolidate redundant connections into cleaner architecture.
Data Structure Complexity: Custom objects and fields accumulated over time that create unnecessary complexity. Evaluate whether these truly need to recreate in HubSpot or if simpler approaches would work better.
Organizations that consciously eliminate technical debt during migration typically emerge with cleaner, more maintainable HubSpot implementations that cost less to operate long-term. However, this requires dedicated planning effort to identify debt and develop remediation strategies.
Building Accurate Timeline and Cost Projections
Component-Based Estimation Approach
Accurate migration timeline and cost projection requires granular, component-based estimation rather than high-level guesswork. Break the migration into distinct workstreams, estimate each independently, then synthesize into comprehensive project plans.
Primary workstreams in most HubSpot migrations include:
Data Migration: Covers data cleansing, mapping specification, transformation development, migration execution, and validation. Estimate based on record volumes, data quality indicators, and mapping complexity.
Asset Rebuilding: Includes recreating email templates, landing pages, forms, and other marketing collateral in HubSpot. Estimate per asset based on complexity tiers established during prioritization.
Workflow and Automation Recreation: Covers rebuilding automation sequences, workflow logic, and business rules. Estimate per workflow based on complexity factors like number of actions, conditional logic branches, and integration dependencies.
Integration Development: Includes reconfiguring native integrations, implementing marketplace solutions, and developing custom integration code. Estimate per integration based on complexity assessment.
Testing and Validation: Covers system testing, user acceptance testing, and data validation. Budget 20-30% of development time for thorough testing—skimping here leads to post-launch firefighting.
Training and Change Management: Includes developing training materials, conducting sessions, and supporting initial user adaptation. Estimate based on user count and complexity of usage scenarios.
Project Management and Coordination: The overhead of keeping the project organized, stakeholders aligned, and issues resolved. Budget 15-20% of technical effort for project management.
Accounting for Known Variables
Several factors predictably influence migration timeline and cost in measurable ways:
Data Volume: More records require more processing time, but the relationship isn't linear. Migrating 500,000 records doesn't take 10x longer than migrating 50,000—economies of scale apply. However, data volume does correlate with increased likelihood of data quality issues that extend timelines.
Platform Complexity: Organizations migrating from Marketo typically face more complexity than those leaving Pardot due to Marketo's greater feature depth and customization capabilities. Platform differences translate directly to increased mapping and translation effort.
Integration Count: Each additional integration adds planning time, development effort, and testing requirements. Projects with 10+ integrations require 30-50% more timeline than those with minimal integration needs.
Customization Depth: Heavily customized current implementations require more effort to translate to HubSpot than relatively vanilla configurations. Extensive custom objects, complex automation logic, and unique workflows all extend timelines.
Organizational Readiness: Companies with strong project management capabilities, available stakeholder time, and clear decision-making processes move faster than those where these elements are lacking.
Building in Appropriate Contingency
Even with thorough planning, unexpected issues emerge during migration. Appropriate contingency buffers prevent these inevitable surprises from derailing projects:
Timeline Contingency: Build 20-25% schedule buffer for unexpected delays, stakeholder feedback cycles, and discovery of unforeseen complexity. This doesn't mean the project takes 25% longer—it means you can absorb normal variations without panic.
Budget Contingency: Reserve 15-20% budget contingency for scope additions, extended consulting needs, or unforeseen technical challenges. Track contingency use carefully—it's not a slush fund but insurance against genuine surprises.
Scope Reserve: Maintain a small scope reserve for must-have additions discovered during execution. Not everything can be anticipated during planning, but uncontrolled scope expansion destroys budgets. A formal scope reserve with approval requirements balances flexibility with control.
Resource Buffer: Maintain access to additional implementation resources who can be mobilized if timelines compress or complexity exceeds estimates. This might be additional consulting days from your implementation partner or internal resources who can be temporarily assigned.
Leveraging Automation for Migration Planning
Automated Asset Discovery and Inventory
Manual migration planning relies on human effort to catalog assets, assess dependencies, and document current state. This process is time-consuming, error-prone, and inevitably incomplete. Modern automated assessment tools transform this foundational planning step.
Automated discovery platforms connect directly to your current marketing automation system and systematically inventory all assets, configurations, and integrations. This automated approach provides several advantages over manual discovery:
Completeness: Automated tools find every asset, including those buried in archive folders or not actively used. Nothing gets overlooked because someone forgot to check a particular location.
Speed: What might take a team several weeks to manually inventory, automated tools complete in hours. This accelerates project timelines and allows planning to begin with complete information.
Accuracy: Automated inventory eliminates human transcription errors, miscounts, and classification mistakes. The resulting data becomes a reliable foundation for planning decisions.
Dependency Mapping: Advanced tools identify relationships between assets—which workflows reference which forms, which emails are triggered by which automation sequences. These dependencies are nearly impossible to map manually but critical for migration planning.
Usage Analytics: Automated tools can analyze asset usage patterns over time, identifying which elements get used regularly versus those that are rarely or never accessed. This data drives strategic prioritization decisions.
Estimator Tools for Accurate Scope Assessment
Modern migration planning tools go beyond simple discovery to provide intelligent analysis and estimation capabilities. These platforms use accumulated experience from hundreds or thousands of migrations to project timeline and effort requirements for your specific scenario.
Sophisticated migration estimators analyze factors including:
Asset Complexity Scoring: Not all email templates or workflows require equivalent effort to rebuild. Estimator tools assess complexity based on factors like element count, conditional logic, dynamic content, and integration dependencies.
Rebuild vs. Archive Recommendations: Based on usage patterns and performance metrics, intelligent tools can suggest which assets deserve migration effort versus those better archived or abandoned.
Effort Projection: Using complexity analysis and benchmark data, estimators project the hours required to migrate each asset category, providing granular bottom-up timeline and cost estimates.
Risk Identification: Advanced tools flag potential migration risks like complex data transformations, ambiguous field mappings, or integration dependencies requiring custom work.
Scenario Planning: The best estimators allow exploring different migration approaches—phased vs. big-bang, minimal vs. comprehensive asset migration—showing timeline and cost implications of each option.
Data Validation and Quality Analysis Automation
Data quality assessment represents another area where automation dramatically outperforms manual analysis. Automated data quality tools scan your entire database to identify:
Duplicate Records: Using sophisticated matching algorithms that go beyond exact matches to identify potential duplicates based on multiple field combinations and fuzzy matching